“If we knew what we were doing, it wouldn’t be called research.”
– Albert Einstein
About Our Lab
Our research group operates within a small yet dedicated laboratory located in the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, at the University of Medicine and Pharmacy in Ho Chi Minh City. We were honored to have previously worked under the visionary and inspiring leadership of Professor Khac-Minh Thai, whose guidance has shaped our scientific endeavors. Building upon this foundation, I am now mentoring both undergraduate and graduate students in conducting drug discovery research. Together, we explore innovative approaches to identify and develop potential therapeutic agents by leveraging the power of modern computational tools and methodologies, even within the modest infrastructure of a developing country like Vietnam.
Mission and Vision
Our mission is to discover and develop bioactive compounds to combat critical diseases, contributing to the advancement of medicinal chemistry and drug discovery. We are especially interested in exploring novel scaffolds from natural compounds found in Vietnamese traditional medicine, harnessing their rich ethnopharmacological potential to create impactful therapies. By integrating computational modeling, cheminformatics, and molecular simulations with experimental validation, we aim to bridge the gap between in silico predictions and real-world drug development.
Our vision is to contribute to the global scientific community by fostering innovation, collaboration, and knowledge-sharing in the field of computational drug discovery.
Research Focus
Our group is deeply interested in and passionate about the screening and design of small molecules that target:
- Protein-protein interactions, with a focus on discovering modulators or inhibitors of key biological pathways involved in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
- Antibacterial targets and other microorganisms, aiming to address the growing challenge of drug resistance.
- Cancer-related targets, exploring novel therapeutic approaches for oncology.
- Metabolic disease targets, including those associated with diabetes, obesity, and dyslipidemia, aiming to identify molecules that can effectively regulate key metabolic pathways.
In parallel, we also focus on the application and evaluation of modern computational approaches – including cheminformatics, molecular modeling, and AI – on selected well-characterized drug targets. Through these efforts, we aim to validate methodologies and develop robust, generalizable pipelines that can accelerate future drug discovery projects.
By integrating both computational and experimental strategies, we strive not only to understand drug-target interactions but also to accelerate the development of innovative therapies for diseases with high unmet medical needs.
Methodologies
Our research group employs a range of advanced methodologies in cheminformatics to facilitate drug discovery and development. These include:
- QSAR modeling, employing both traditional statistical techniques and advanced machine learning and deep learning methods to predict the biological activity of compounds.
- Pharmacophore modeling (both ligand-based and structure-based), to identify key features essential for molecular recognition.
- Similarity searching, to identify compounds with comparable structures that may exhibit improved biological activity.
- Binding site detection, with a focus on allosteric sites and cryptic pockets, utilizing geometry-based, energy-based, and machine learning-driven approaches to identify novel druggable regions.
- Molecular docking, including high-throughput virtual screening and machine learning-assisted docking, to predict binding modes and affinities of compounds.
- Molecular dynamics simulations, to study the dynamic behavior of biomolecular systems and evaluate ligand stability.
- Binding free energy calculations using MM-PBSA and MM-GBSA, to estimate protein-ligand binding affinities.
- ADMET profiling, to assess the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity properties of potential drug candidates.
- AI-driven drug discovery, leveraging deep learning and generative models to accelerate the identification and optimization of promising drug candidates.
By integrating these methodologies, we aim to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of drug discovery, identifying promising candidates for further development.
Our Work
Our Team

Lab Members
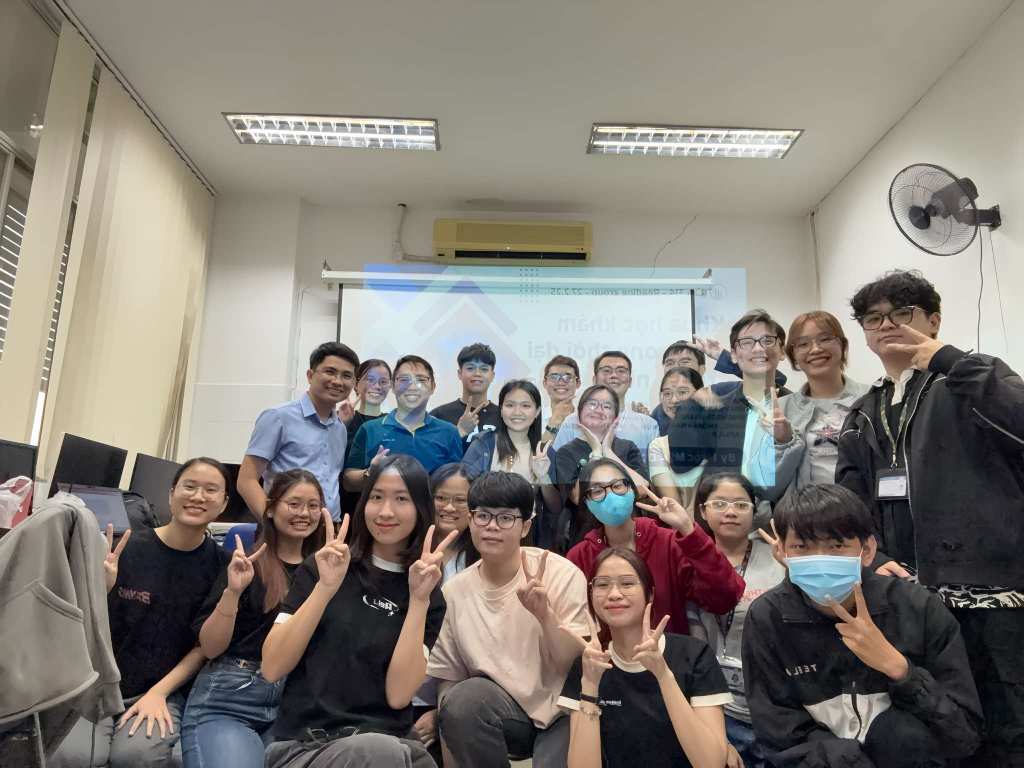
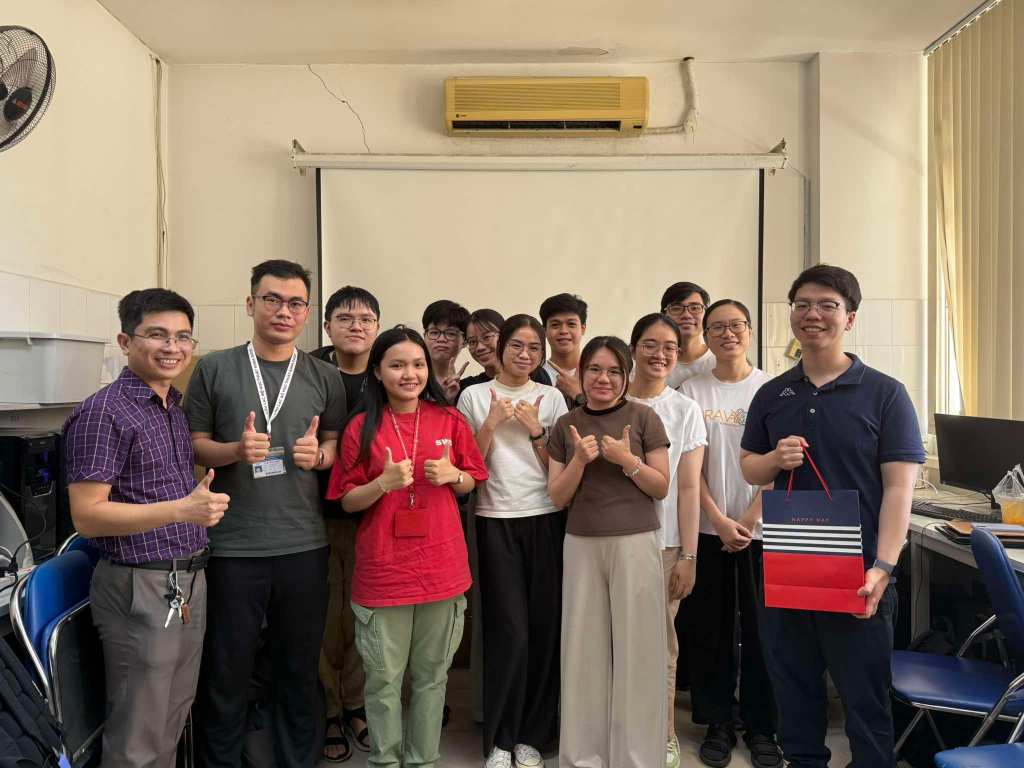
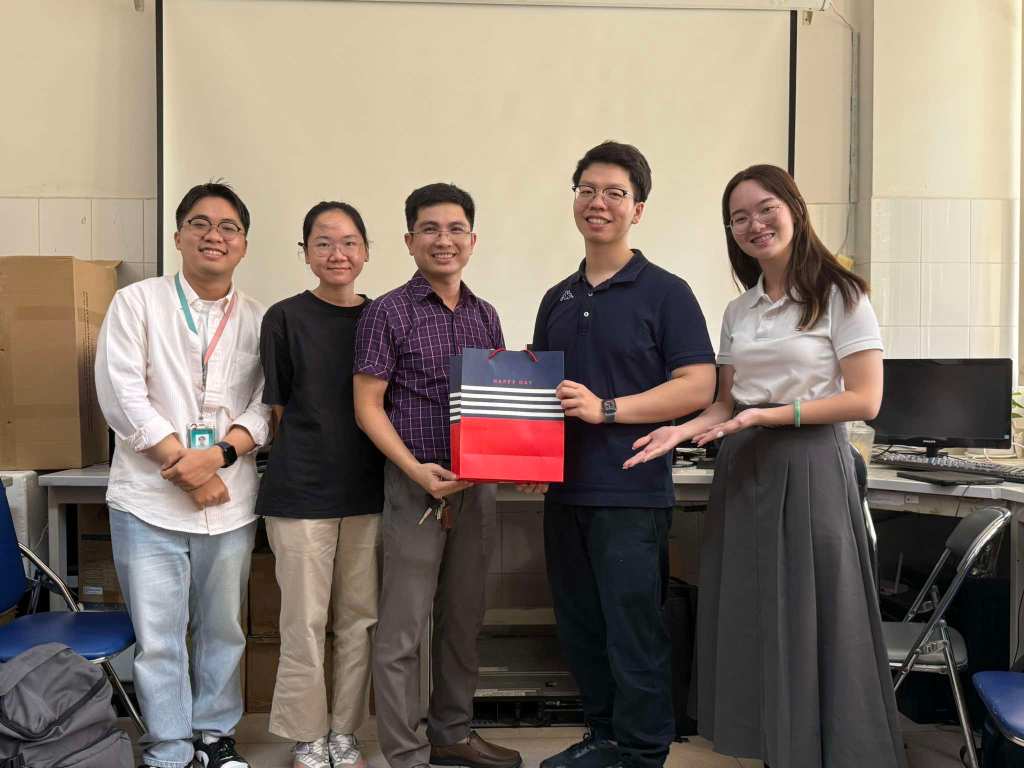
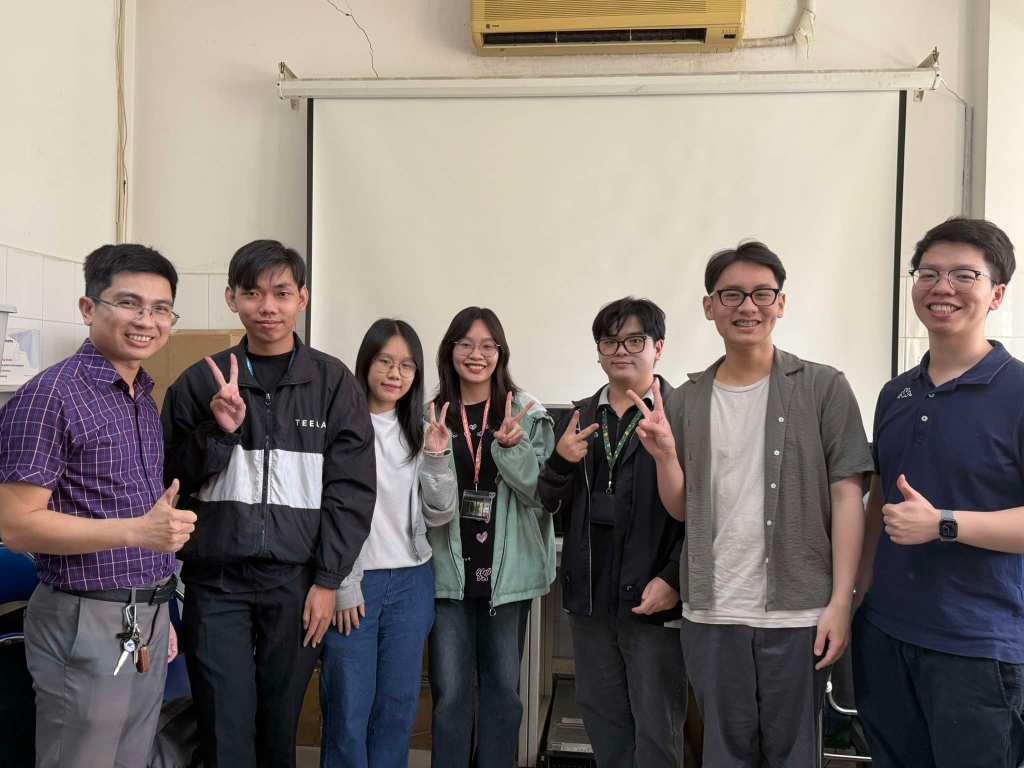
Below are the members of our lab, both current students and alumni, who have engaged in rigorous study, skill development, and meaningful contributions to our research efforts. Their dedication has played a crucial role in advancing our scientific endeavors.
Current Lab Members
Graduate Students
Undergraduates
Alumni
Lab Memories
Lab Meeting
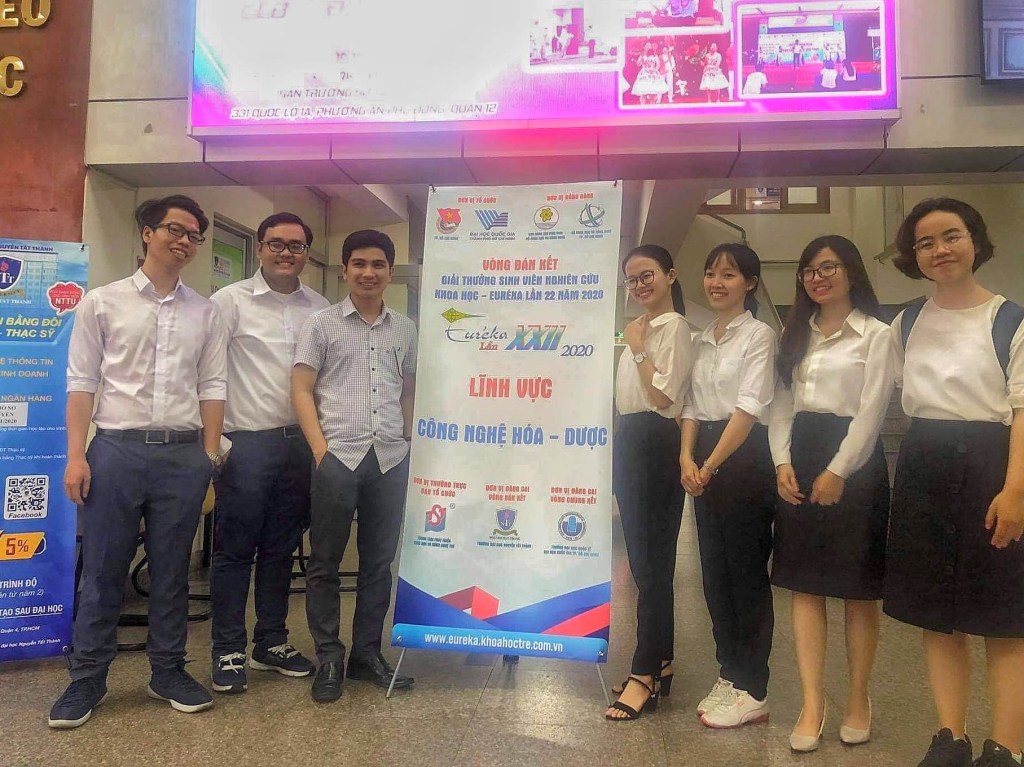
Conference Participation
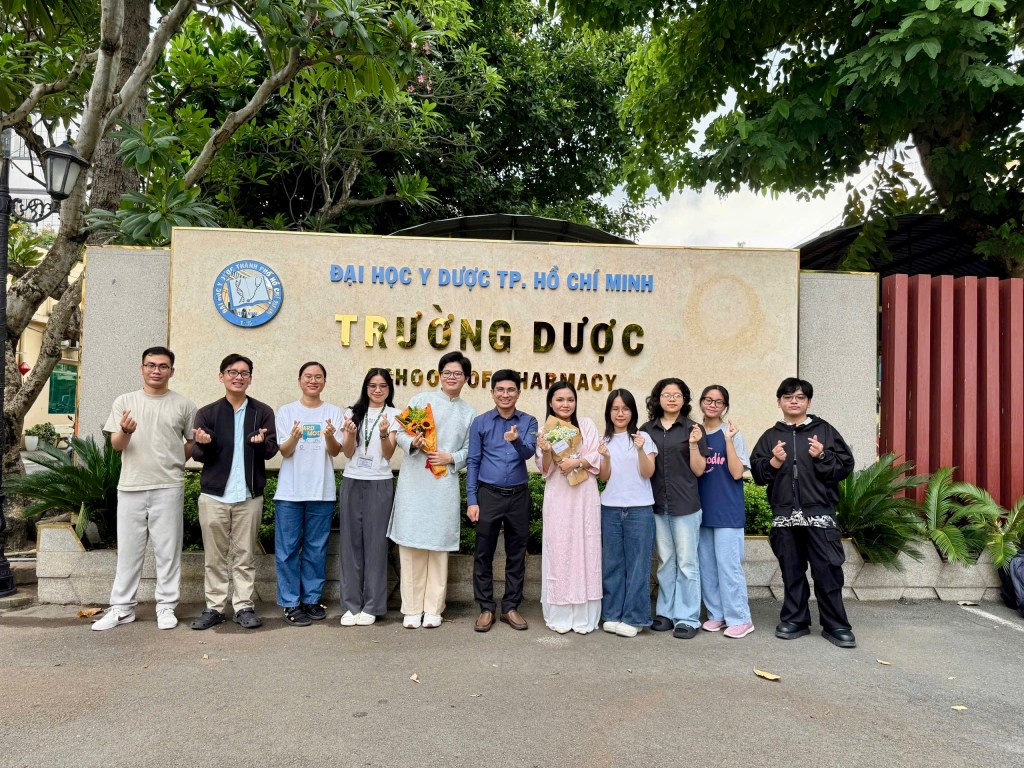
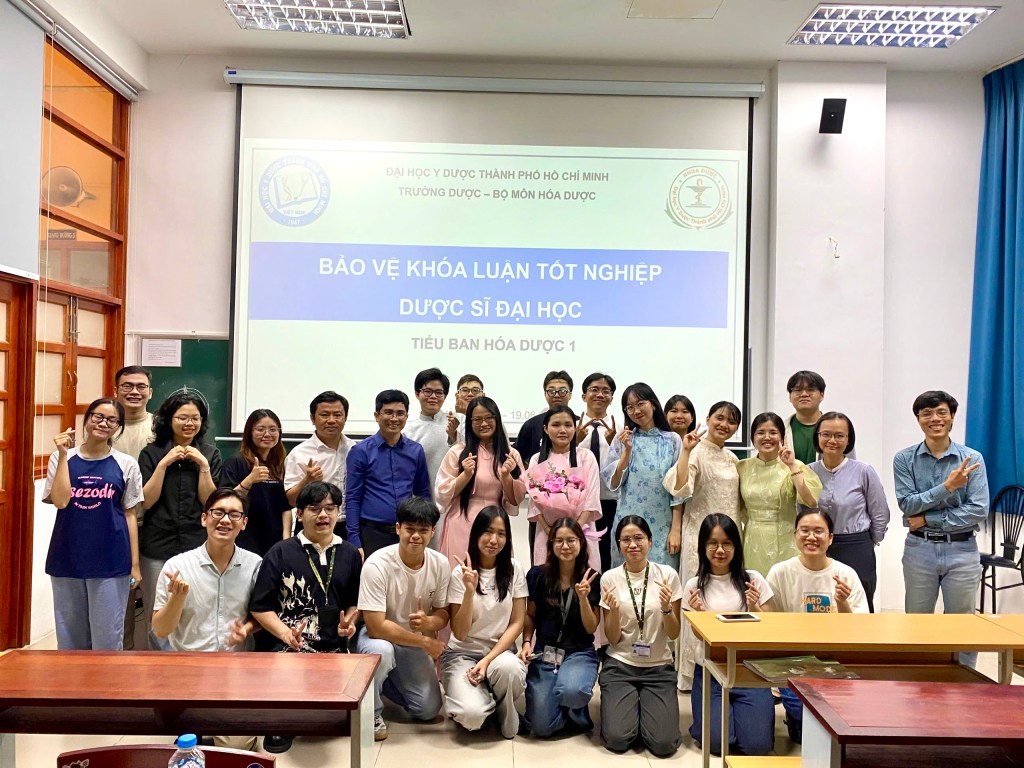
Graduation Defense
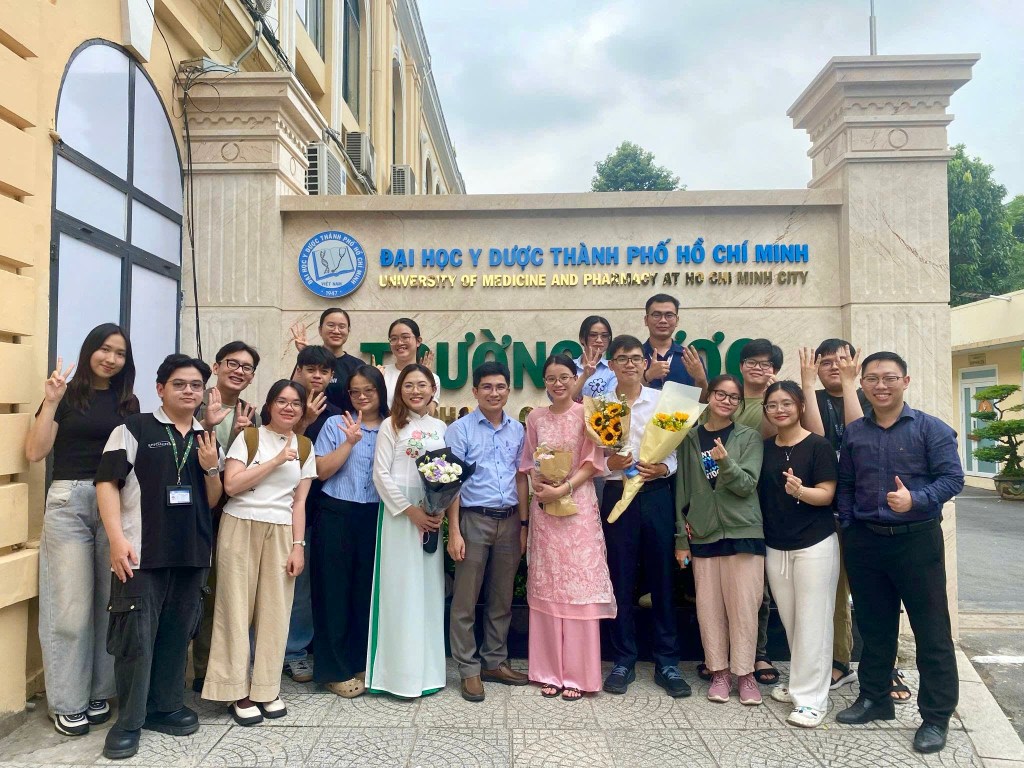
Graduation Ceremony
Lab Parties
Internal Lab Activities
For Lab Members Only
Collaboration Opportunities
We welcome collaborations with groups specializing in cheminformatics and virtual screening, as well as those conducting experimental research, including chemical synthesis and biological activity evaluation. Our computational modeling and simulation approaches can complement your work on disease-related targets by interpreting experimental results, guiding the synthesis process, and optimizing hit or lead compounds.
We are also honored to collaborate with researchers in natural product studies, helping to identify potential molecular targets for your natural compounds. Together, we can explore the possibility of developing new drug candidates from your fascinating natural scaffolds.
Let’s join forces to advance science and contribute to impactful discoveries!
Visit us
Room 314, Five-Story Building, School of Pharmacy,
University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh City
41 Dinh Tien Hoang Street,
Sai Gon Ward, Ho Chi Minh City 70000, Vietnam
Hours
Monday – Friday
8:00 AM – 5:00 PM
Phone
(+84) 28 38 295 641 – 117
“Great discoveries and improvements invariably involve the cooperation of many minds.”
– Alexander Graham Bell